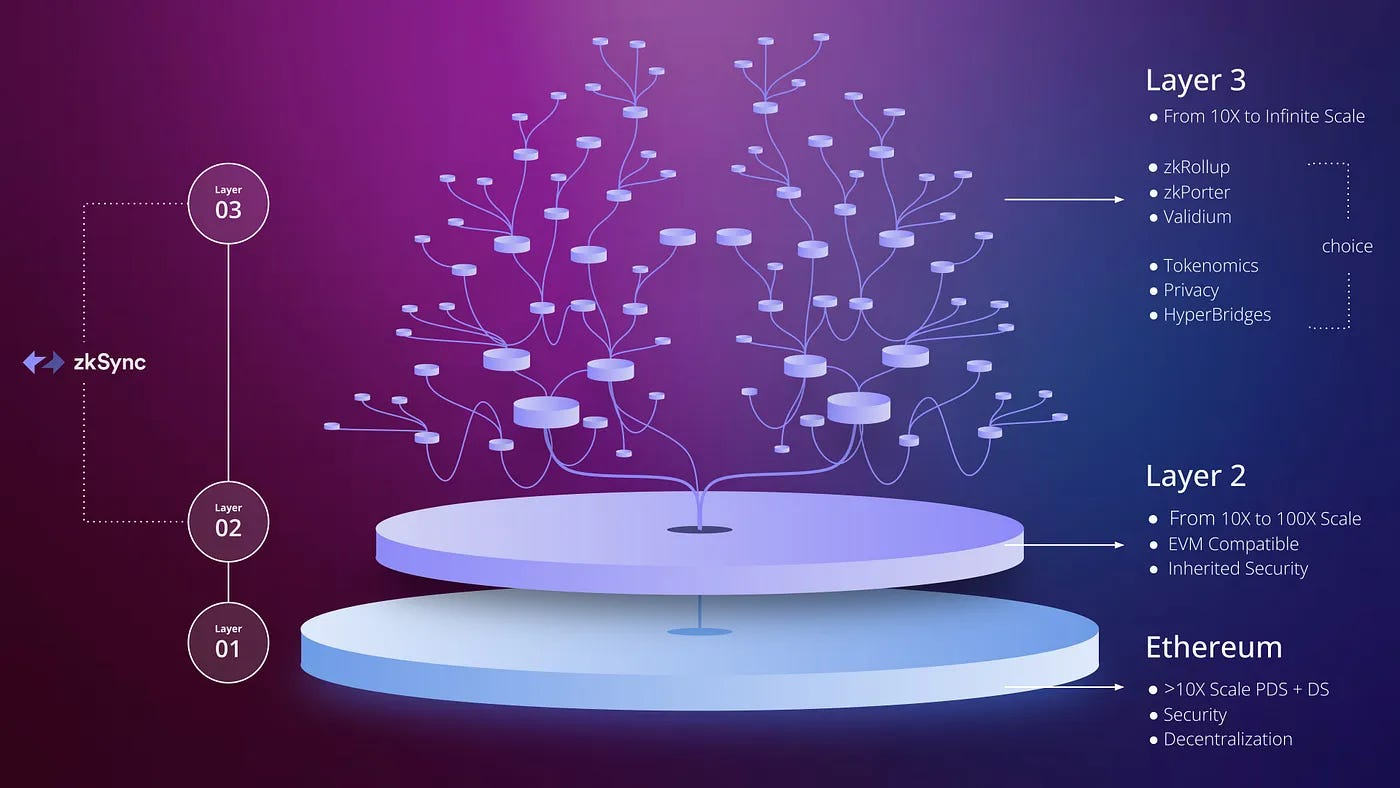
As Bitcoin continues to solidify its position as the most secure and widely adopted cryptocurrency, the focus is increasingly shifting to interoperability and cross-chain innovation. Layer-2 solutions like Lightning Network have addressed scalability, but the next frontier—Layer-3 protocols—aims to enable seamless interaction between Bitcoin, other blockchain networks, and decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems. Layer-3 solutions promise cross-chain liquidity, decentralized applications (dApps) on Bitcoin, and integrated financial services, making Bitcoin not just a store of value but a foundation for a fully interconnected digital economy.
Interoperability has become a core concern for the crypto ecosystem. While Bitcoin dominates as a secure, decentralized, and highly liquid network, most DeFi activity has historically occurred on Ethereum or similar smart contract platforms. Layer-3 solutions seek to bridge these networks, unlocking new use cases, enhancing adoption, and creating a richer financial ecosystem for both retail and institutional users.
Understanding Layer-3 and Cross-Chain Protocols
Layer-3 refers to protocols built on top of Layer-2 networks that facilitate cross-chain communication and decentralized applications:
- Cross-Chain Bridges: Enable assets and data to move between Bitcoin and other blockchains securely.
- Composable Financial Applications: Allow Bitcoin to participate in DeFi services such as lending, borrowing, and automated market-making.
- Integrated dApps: Decentralized applications that leverage Bitcoin for collateral, payments, or value transfer across multiple chains.
The goal of Layer-3 is to maintain Bitcoin’s security while expanding its functional utility in the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Why Interoperability Matters
Bitcoin interoperability addresses several key challenges:
- Liquidity Fragmentation
Currently, Bitcoin’s liquidity is mostly confined to its native network, limiting DeFi integration. Cross-chain solutions unlock Bitcoin’s capital for decentralized applications, improving efficiency. - Cross-Chain DeFi Access
Users can leverage Bitcoin as collateral for lending, derivatives, and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) on Ethereum, Polygon, and other networks. - Enhanced Utility
Interoperability allows Bitcoin to function as both a store of value and a medium of exchange in programmable finance, increasing adoption and network relevance.
By enabling seamless communication between blockchains, Layer-3 solutions transform Bitcoin from a standalone asset into a versatile financial building block.
Emerging Layer-3 Technologies
Several technologies and protocols are advancing Bitcoin Layer-3 and interoperability:
- Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC, tBTC, etc.)
Tokenized versions of Bitcoin on Ethereum allow Bitcoin holders to participate in Ethereum DeFi, maintaining exposure to Bitcoin’s value while accessing smart contracts. - Cross-Chain Bridges
Protocols like RenBridge, ThorChain, and Interlay enable secure, decentralized asset transfers across Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other networks, facilitating liquidity movement. - Layer-2 Aggregators
Platforms integrating multiple Layer-2 networks allow Bitcoin to interact indirectly with smart contracts and DeFi protocols, reducing friction and cost. - Atomic Swaps
Trustless peer-to-peer exchanges allow Bitcoin to be exchanged directly for other cryptocurrencies without intermediaries, enhancing liquidity and interoperability.
These technologies collectively enhance Bitcoin’s integration into the broader DeFi ecosystem, providing new financial opportunities for users and developers.
Benefits of Layer-3 Integration
Layer-3 solutions provide multiple advantages:
- DeFi Access for Bitcoin Holders: Enables lending, borrowing, yield farming, and synthetic assets using Bitcoin as collateral.
- Cross-Chain Liquidity: Moves capital across blockchains efficiently, reducing friction and increasing market depth.
- Enhanced Network Utility: Bitcoin becomes more than a store of value; it powers decentralized financial products and services.
- Innovation in Smart Contracts: Layer-3 protocols create opportunities for smart contracts to leverage Bitcoin’s liquidity without compromising security.
By enhancing utility while maintaining Bitcoin’s decentralization, Layer-3 protocols strengthen both the Bitcoin ecosystem and the wider blockchain landscape.
Case Studies in Cross-Chain DeFi
Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC)
WBTC is an ERC-20 token pegged 1:1 to Bitcoin, allowing holders to participate in Ethereum-based DeFi platforms. WBTC has unlocked billions in liquidity, demonstrating Bitcoin’s functional potential in smart contract ecosystems.
RenBridge
RenBridge enables trustless transfers of Bitcoin to Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and other networks. Its decentralized architecture highlights the possibility of secure cross-chain interoperability.
ThorChain
ThorChain provides decentralized liquidity pools across multiple blockchains, including Bitcoin, allowing native Bitcoin users to trade and lend without wrapping or intermediaries. This model showcases true cross-chain DeFi integration.
These examples demonstrate how Layer-3 protocols enable Bitcoin to participate in complex financial ecosystems while preserving security and decentralization.
Security Considerations
While Layer-3 solutions expand Bitcoin’s functionality, they also introduce security risks:
- Bridge Vulnerabilities: Cross-chain protocols may be susceptible to smart contract bugs or exploits.
- Custodial Risks: Wrapped or tokenized Bitcoin may require custodial or semi-custodial mechanisms, introducing counterparty risk.
- Complexity and User Error: Interacting with multiple chains can be confusing, increasing the potential for mistakes or lost funds.
Mitigating these risks requires robust audits, decentralized governance, and user education. Successful Layer-3 protocols balance innovation with security to maintain trust.
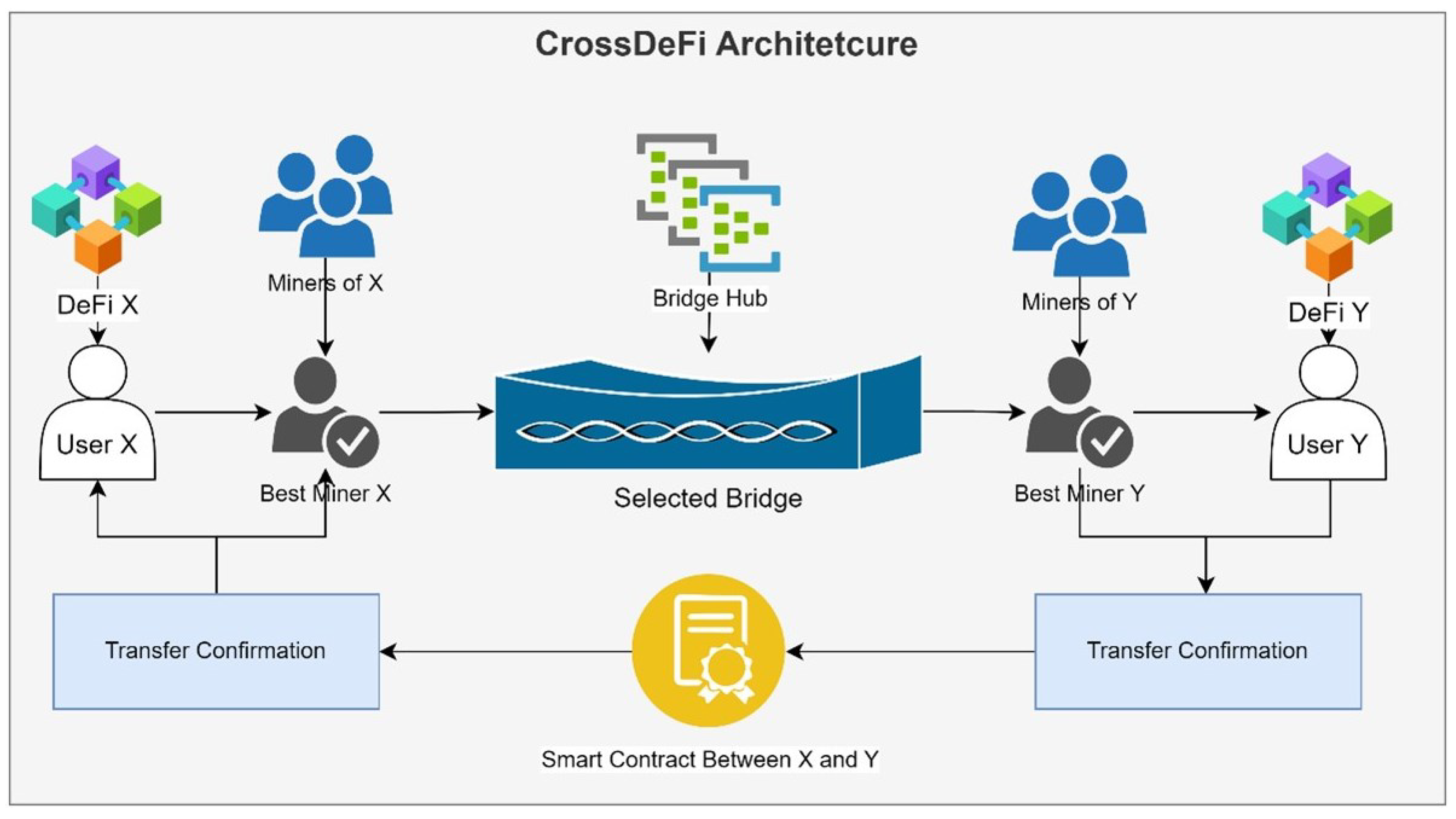
Future Implications
The rise of Bitcoin Layer-3 and interoperability has several long-term implications:
- Expanded DeFi Ecosystem
Bitcoin can serve as collateral, liquidity, and a medium of exchange in complex financial products, increasing its relevance beyond a store of value. - Increased Adoption
Cross-chain integration simplifies access for institutional and retail users, driving broader adoption of Bitcoin in decentralized finance. - Innovation in Payments
Layer-3 enables Bitcoin-powered payment solutions across chains, integrating seamlessly with merchant services and digital wallets. - Global Financial Integration
Bitcoin becomes a bridge between traditional finance, decentralized finance, and cross-border payments, strengthening its role as a global digital asset.
Layer-3 is not just a technical enhancement—it redefines Bitcoin’s potential as an interoperable, programmable, and globally accessible financial system.
Practical Steps for Users
To participate in Layer-3 and cross-chain DeFi safely:
- Use Audited Bridges: Ensure the protocols you interact with are thoroughly audited and widely used.
- Understand Wrapped Assets: Recognize the difference between native Bitcoin and tokenized versions on other chains.
- Diversify Across Platforms: Spread exposure to reduce risk from single-point failures or exploits.
- Stay Educated on DeFi Risks: Monitor network developments, liquidity risks, and protocol vulnerabilities.
By following these steps, Bitcoin holders can leverage Layer-3 innovations without compromising security.
Final Thoughts
Layer-3 and interoperability mark the next evolution of Bitcoin, moving it beyond a decentralized currency into a foundation for cross-chain decentralized finance. Through bridges, wrapped assets, Layer-2 aggregators, and atomic swaps, Bitcoin becomes a versatile financial instrument, capable of powering DeFi applications, cross-chain liquidity, and global financial networks.
While challenges remain—particularly in security, complexity, and regulatory alignment—the promise of Layer-3 is clear: Bitcoin can participate fully in the decentralized finance ecosystem, unlocking new use cases, liquidity channels, and investment opportunities. The future of Bitcoin is not only as a store of value but as a globally interoperable financial backbone, bridging traditional finance and decentralized innovation in ways that were previously impossible.