Bitcoin’s supply schedule is one of its most distinctive features. Every 210,000 blocks — roughly every four years — the Bitcoin network undergoes a halving event, reducing the reward miners receive for validating transactions by 50%. This built-in scarcity mechanism affects supply, market sentiment, and investor behavior. Understanding how halving events influence price cycles is essential for both short-term traders and long-term holders seeking to optimize strategy.
Since Bitcoin’s inception in 2009, halvings have repeatedly proven to be major catalysts for market movement, influencing adoption, media attention, and institutional interest. The phenomenon is unique among financial assets and underscores Bitcoin’s design as a deflationary digital currency.
What Is a Bitcoin Halving?
A Bitcoin halving occurs as part of the network’s protocol. It:
- Reduces the block reward by 50%, cutting the rate at which new Bitcoin enters circulation.
- Occurs approximately every four years, ensuring predictable and decreasing inflation.
- Reinforces Bitcoin’s scarcity, enhancing its value proposition as digital gold.
For example, the first halving in 2012 reduced the block reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC, the 2016 halving reduced it to 12.5 BTC, and the 2020 halving reduced it to 6.25 BTC per block. The next halving, expected in 2024, will further reduce rewards to 3.125 BTC, tightening supply and potentially influencing price.
Historical Impact on Bitcoin Prices
Analyzing previous halving events provides insight into how these events affect price cycles:
- 2012 Halving
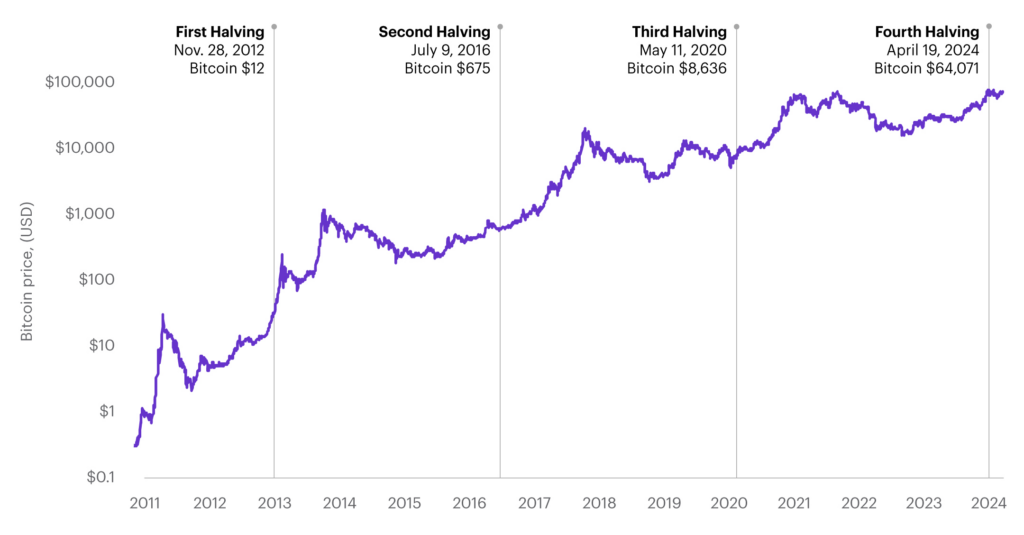
After the first halving, Bitcoin entered a significant bull market, rising from around $12 to over $1,100 in late 2013. The reduction in new supply created scarcity, which combined with growing adoption and media coverage to drive prices higher. - 2016 Halving
Bitcoin’s second halving reduced the block reward to 12.5 BTC. Prices remained relatively stable immediately but surged in 2017, reaching nearly $20,000 by December. This lag between halving and price peak illustrates the market’s gradual absorption of reduced supply. - 2020 Halving
The third halving reduced rewards to 6.25 BTC per block. Prices were around $8,800 at the time of the event and surged to over $64,000 by April 2021. The combination of scarcity, institutional investment, and macroeconomic stimulus amplified the post-halving rally.
Historical trends suggest that while halving does not immediately cause a price spike, it significantly influences long-term market cycles.
How Halvings Affect Investor Behavior
Halving events influence psychology, strategy, and market participation:
- Increased Media Attention: Halvings often attract mainstream media coverage, drawing new investors and capital into Bitcoin.
- FOMO and Speculation: Anticipation of post-halving price increases can trigger speculative buying months in advance.
- Long-Term Accumulation: Many investors use halving events as a cue to increase holdings in anticipation of future scarcity-driven price appreciation.
Halvings serve as predictable milestones, allowing investors to align strategy with structural market factors rather than reacting purely to short-term news.
Supply Shock and Price Dynamics
Bitcoin’s halvings are often described as supply shocks:
- The immediate reduction in new supply limits selling pressure from miners, potentially supporting prices if demand remains stable or increases.
- Markets tend to price in expected halvings months in advance, but surprises or macroeconomic conditions can amplify volatility.
- Scarcity-driven narratives reinforce investor belief in Bitcoin as digital gold, enhancing accumulation behavior.
Supply shock theory suggests that Bitcoin’s decreasing inflation rate post-halving contributes to its long-term appreciation trajectory.
Portfolio Strategies Around Halvings
Investors often adjust their approach before, during, and after halving events:
- Pre-Halving Accumulation
Accumulating Bitcoin 6–12 months before a halving is a common strategy, anticipating scarcity effects on price. - Post-Halving Hold
Many investors adopt a buy-and-hold approach after the halving, focusing on long-term capital appreciation rather than short-term trading. - Risk Management
Halvings can introduce volatility. Maintaining a diversified portfolio or using stop-loss mechanisms can mitigate potential downside risk.
These strategies highlight the importance of understanding the structural nature of Bitcoin’s supply schedule.
Halvings and Market Cycles
Bitcoin’s price movements often align with a repeating market cycle influenced by halving events:
- Accumulation Phase: Occurs before halving as smart money and early adopters increase holdings.
- Mark-Up Phase: Post-halving period where prices trend upward, fueled by scarcity, adoption, and media attention.
- Distribution Phase: After peak prices, investors take profits, leading to market corrections.
- Accumulation Phase Restart: The cycle repeats, aligned with the next halving.
Understanding this cyclical pattern allows investors to anticipate potential highs and lows, balancing risk and reward over multiple market cycles.
Institutional Adoption and Halvings
Institutional interest in Bitcoin often intensifies around halving events:
- Corporations, hedge funds, and ETFs increasingly allocate capital in anticipation of scarcity-driven rallies.
- Media coverage and public awareness contribute to institutional FOMO, creating additional upward pressure on prices.
- Halvings reinforce Bitcoin’s narrative as digital gold, encouraging allocation for treasury management and portfolio diversification.
Institutional participation amplifies the market impact of halving events compared to previous cycles, creating more predictable patterns for strategic investors.
Risks and Considerations
While halvings historically correlate with bullish cycles, risks remain:
- External Market Forces: Macroeconomic events, regulatory actions, and technological disruptions can override halving dynamics.
- Price Volatility: Immediate post-halving periods can see temporary dips or sideways movement before upward trends materialize.
- Psychological Overconfidence: Overreliance on halving cycles can lead to speculative bubbles or mistimed entries.
Investors must balance halving-driven strategies with broader market analysis and risk management techniques.
Final Thoughts
Bitcoin halvings are central to its economic model, creating predictable scarcity that influences price cycles, market psychology, and investor behavior. By understanding historical patterns and supply dynamics, investors can align strategies to take advantage of structural trends while managing risk.
Halvings reinforce Bitcoin’s role as digital gold, creating long-term value through limited supply and network effects. For long-term holders, these events offer strategic accumulation opportunities, while traders can use market cycles to optimize timing.
In an increasingly global and decentralized financial system, understanding halving dynamics is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate Bitcoin’s volatile but historically rewarding market. With the next halving approaching, awareness of supply shocks, investor psychology, and institutional behavior will remain key to making informed, strategic decisions in the evolving crypto landscape. If you want to be rich, don’t waste this opportunity, later you will be proud of you.
