Bitcoin has revolutionized finance by providing a decentralized and permissionless system for transferring and storing value. However, with great autonomy comes great responsibility. The security of your Bitcoin holdings is entirely in your hands. Unlike traditional banking, where institutions manage custody and provide recourse in case of theft or loss, Bitcoin ownership is self-sovereign: control over private keys equals control over your wealth.
This article explores the security landscape of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, the risks inherent in digital asset ownership, strategies to safeguard wealth, and best practices for long-term protection in a volatile and rapidly evolving ecosystem. Understanding security is essential for anyone who wants to hold Bitcoin confidently, especially as institutional and retail adoption continues to grow.
The Importance of Self-Sovereignty
Bitcoin’s foundational principle is decentralization. Unlike fiat currencies, which are issued and controlled by governments, Bitcoin operates on a blockchain network maintained by nodes and miners worldwide. Ownership is determined by private keys—a cryptographic proof that only the holder can spend or transfer coins.
This structure eliminates the need for intermediaries, but it also eliminates safety nets. Losing access to your keys means permanent loss of funds. Hacks, phishing attacks, and human error are all risks that can compromise your holdings. In this sense, Bitcoin security is not optional; it is the foundation upon which all investment strategy rests.
Common Security Risks
Bitcoin holders face several categories of security risks:
- Exchange Risks: Leaving funds on centralized exchanges exposes users to hacks, insolvency, or mismanagement. Historical examples include Mt. Gox, QuadrigaCX, and FTX, where billions of dollars in customer funds were lost or frozen.
- Phishing Attacks: Malicious actors impersonate wallets, exchanges, or platforms to steal credentials or trick users into revealing private keys.
- Malware and Keyloggers: Computers or devices infected with malware can compromise private keys or seed phrases.
- Physical Theft: Hardware wallets or written backups can be stolen if not stored securely.
- Human Error: Losing seed phrases, sending Bitcoin to incorrect addresses, or mishandling backups results in permanent loss.
Each risk requires proactive management, combining both technological and behavioral safeguards.
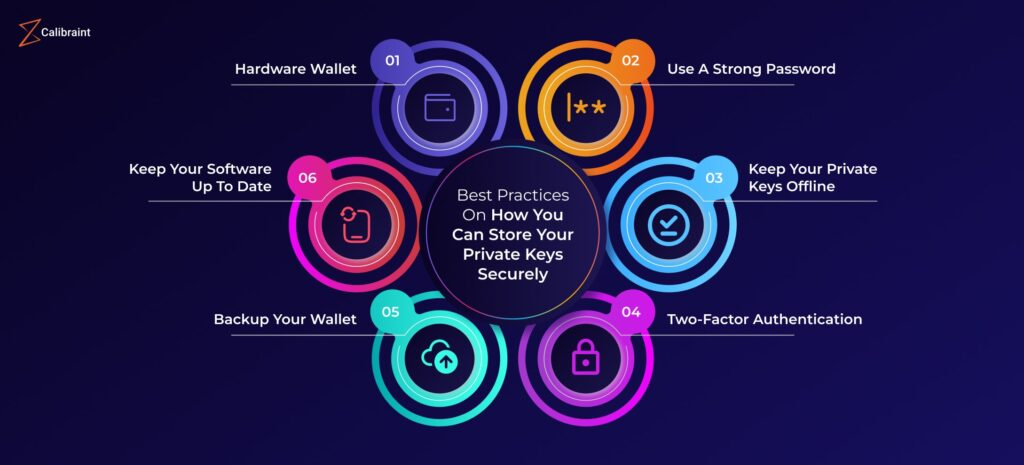
Self-Custody Solutions
To mitigate these risks, Bitcoin holders should prioritize self-custody, storing private keys independently of third-party institutions. There are several approaches:
- Hardware Wallets: Devices like Ledger or Trezor store keys offline, isolated from internet access, minimizing hacking risk.
- Cold Storage: Keeping Bitcoin entirely offline reduces exposure to malware and online attacks.
- Multi-Signature Wallets: Requiring multiple signatures to authorize transactions provides redundancy and reduces single-point-of-failure risk.
- Seed Phrase Security: Backing up recovery phrases in multiple secure locations, ideally using fireproof and waterproof storage, ensures recovery in case of loss or damage.
Self-custody transforms Bitcoin ownership from a dependency on institutions to true financial sovereignty.
Network-Level Security
Bitcoin’s security is not only about individual wallets—it is reinforced by the network itself:
- Decentralized Verification: Thousands of independent nodes validate transactions, preventing manipulation by any single party.
- Proof-of-Work Mining: The energy-intensive mining process secures the network against attacks. The cost and complexity of attacking Bitcoin makes large-scale tampering economically infeasible.
- Consensus Rules: Changes to the Bitcoin protocol require agreement across the network, protecting against arbitrary alterations.
This layered security makes Bitcoin resilient and trustworthy, even in the face of global financial uncertainty.
Security Best Practices
Bitcoin holders should adopt a comprehensive security strategy:
- Use Hardware Wallets for Long-Term Holdings: Keep small amounts in hot wallets for daily transactions, but store the majority offline.
- Diversify Storage Methods: Avoid keeping all coins in a single device or location.
- Regularly Update Devices and Software: Security vulnerabilities can arise from outdated firmware or wallet applications.
- Education and Vigilance: Recognize phishing attempts, malicious software, and social engineering tactics. Knowledge is the most effective defense.
- Multi-Signature Strategies: Consider multi-party authorization for large holdings to mitigate single-point-of-failure risks.
By combining technology, procedural discipline, and awareness, holders can secure Bitcoin against both digital and physical threats.
Institutional Security and Custody
As institutional adoption grows, the demand for secure custody solutions has skyrocketed. Institutions cannot risk losses through hacks or mismanagement, so companies such as Fidelity Digital Assets, BitGo, and Coinbase Custody provide regulated custody solutions with advanced security protocols. These services often incorporate multi-signature schemes, insurance coverage, and operational controls suitable for professional investment.
While these services provide convenience and insurance, self-custody remains a fundamental skill for any individual investor. Understanding the principles behind secure storage ensures independence from third-party failures and reinforces long-term financial sovereignty.
Psychological Implications
Security in Bitcoin is not merely technical—it shapes investor psychology. Confident holders who understand self-custody are less likely to panic sell during volatility, as they are assured that assets are safe. Conversely, those relying on exchanges or unsecured storage may react impulsively to price swings, undermining long-term strategy.
Security awareness fosters discipline, patience, and a mindset aligned with Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition. It also emphasizes responsibility, as true ownership comes with accountability.
Conclusion
Bitcoin security is the foundation of all successful investment strategies. Unlike traditional banking, there are no third-party safety nets. Ownership is determined entirely by control of private keys, making self-custody, hardware wallets, multi-signature strategies, and proper backup procedures essential.
Network-level protections, including decentralized verification, proof-of-work mining, and consensus rules, provide resilience against global threats. However, individual diligence remains paramount. Investors who embrace security best practices gain true sovereignty, peace of mind, and the ability to hold Bitcoin confidently through market cycles.
In the digital age, safeguarding your wealth is not optional. Bitcoin offers unprecedented autonomy, but with it comes responsibility. The most critical investment you make is not in price appreciation—it is in securing your keys and protecting your digital assets.
